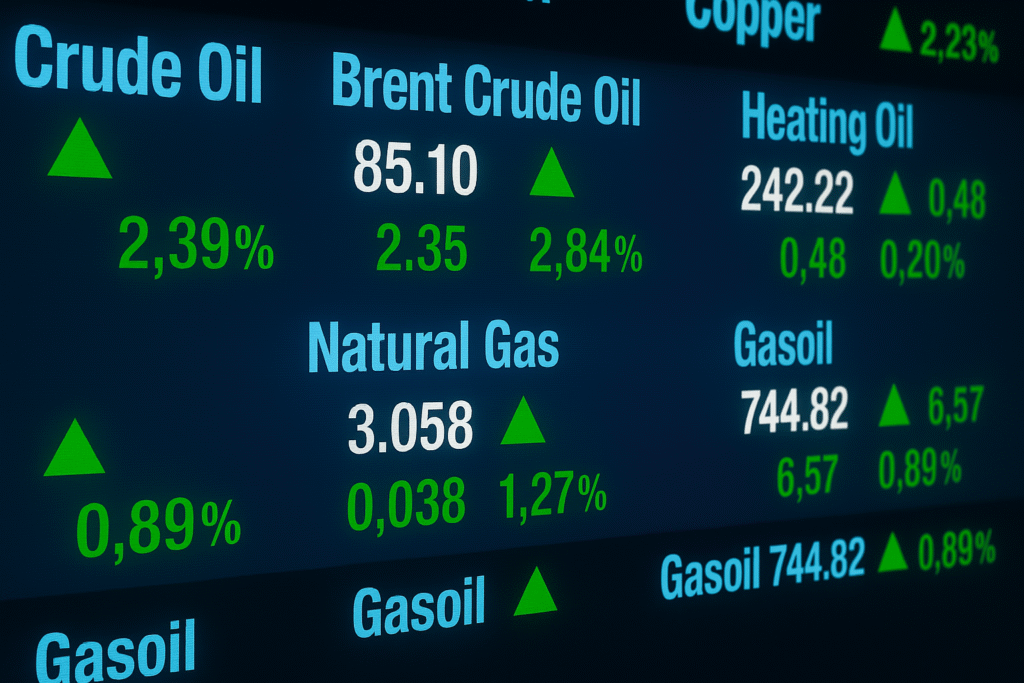
Have you ever wondered how seasoned investors seem to weather economic storms and come out on top? 🤔
The secret might lie in an often-overlooked investment avenue: investing in commodities.
From gold and oil to coffee and wheat, commodity investing taps into the building blocks of our global economy—offering unique opportunities for savvy investors.
But let’s face it – the world of commodity investing can seem daunting to newcomers. Where do you start? How do you navigate the volatile markets? What strategies should you employ? If these questions have been swirling in your mind, you’re in the right place. This beginner’s guide will demystify the process of investing in commodities, equipping you with the knowledge to potentially diversify your portfolio and tap into this exciting market.
👉 For a deeper dive into market insights, visit Investopedia’s Commodity Investing Guide
In the following sections, we’ll dive deep into the essentials of commodity investing. We’ll explore everything from understanding what commodities are and the various investment options available, to analyzing markets and implementing effective strategies. Whether you’re a complete novice or looking to refine your approach, this guide will walk you through each step of your commodity investment journey. So, let’s embark on this adventure and unlock the potential of commodity investing together! 💼📈
Understanding Commodities

A. Definition and types of commodities
Commodities are raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold. They are typically divided into four main categories:
- Energy
- Metals
- Agriculture
- Livestock
Here’s a breakdown of common commodities within each category:
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Energy | Crude oil, natural gas, gasoline, heating oil |
| Metals | Gold, silver, copper, platinum, aluminum |
| Agriculture | Wheat, corn, soybeans, coffee, cotton, sugar |
| Livestock | Live cattle, feeder cattle, lean hogs |
B. Why invest in commodities
Investing in commodities offers several benefits:
- Diversification: Commodities often move independently of stocks and bonds
- Inflation hedge: Commodity prices typically rise with inflation
- Potential for high returns: Commodities can experience significant price swings
- Global economic exposure: Commodities are influenced by worldwide supply and demand
C. Commodity markets explained
Investing in commodities often involves commodity trading through futures contracts—agreements to buy or sell a specific amount of a commodity at a set price on a future date. These markets include:
- Exchanges: Centralized marketplaces where commodities are traded
- Over-the-counter (OTC) markets: Direct trading between buyers and sellers
- Spot markets: Immediate delivery of physical commodities
D. Risks and rewards
Commodity investing comes with unique risks and potential rewards:
Risks:
- High volatility
- Geopolitical factors
- Weather-related events
- Currency fluctuations
Rewards:
- Potential for significant profits
- Portfolio diversification
- Hedge against inflation
Understanding these fundamental aspects of commodities is crucial before delving into specific investment options. Next, we’ll explore the various ways you can invest in commodities, from direct ownership to commodity-linked securities.
Popular Commodity Investment Options
A. Futures contracts
Futures contracts are a popular way to invest in commodities, offering investors the ability to speculate on future prices. These agreements allow buyers to purchase a specific amount of a commodity at a predetermined price on a future date. Here’s a breakdown of key features:
- Standardized contracts
- High leverage potential
- Requires margin account
- Settlement can be physical or cash
B. Stocks of commodity-producing companies
Investing in stocks of companies that produce or process commodities is an indirect way to gain exposure to the commodity market. This method offers:
- Potential for dividends
- Easier to trade than futures
- Exposure to company management and operations
C. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
ETFs provide a simple way to invest in a basket of commodity-related assets. They offer:
- Diversification across multiple commodities
- Lower costs compared to mutual funds
- Easy to buy and sell like stocks
D. Physical commodity ownership
Some investors prefer to own physical commodities, particularly precious metals. This method:
- Provides tangible assets
- Requires secure storage
- May involve additional costs for insurance and storage
E. Mutual funds
Commodity mutual funds offer professional management and diversification. Key features include:
- Active management by professionals
- Diversification across multiple commodities or companies
- Higher fees compared to ETFs
| Investment Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Futures contracts | High leverage, direct exposure | Complex, high risk |
| Stocks | Potential dividends, familiar | Indirect exposure |
| ETFs | Diversification, low cost | May track indexes imperfectly |
| Physical ownership | Tangible asset | Storage and security concerns |
| Mutual funds | Professional management | Higher fees |
Now that we’ve explored various commodity investment options, let’s delve into effective strategies for commodity investing to maximize your potential returns.
Strategies for Commodity Investing

Diversification benefits
Investing in commodities can add significant diversification to your portfolio.
Raw material investing often shows low correlation with traditional assets like stocks and bonds, helping reduce overall risk.
Here’s a comparison of how commodities perform in different economic scenarios:
| Economic Scenario | Stocks | Bonds | Commodities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic Growth | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Recession | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ |
| Inflation | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Deflation | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ |
Long-term vs. short-term approaches
When investing in commodities, consider both long-term and short-term strategies:
- Long-term: Focus on fundamental supply and demand factors, global economic trends, and cyclical patterns.
- Short-term: Capitalize on price volatility, seasonal fluctuations, and market sentiment.
Dollar-cost averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is an effective strategy for commodity investing, especially for beginners. This approach involves:
- Investing a fixed amount regularly
- Buying more units when prices are low
- Buying fewer units when prices are high
- Reducing the impact of market volatility over time
Technical analysis techniques
Technical analysis can be a powerful tool for commodity investors. Key techniques include:
- Trend analysis using moving averages
- Support and resistance levels identification
- Volume analysis to confirm price movements
- Fibonacci retracements for potential reversal points
By combining these strategies, investors can develop a well-rounded approach to commodity investing that balances risk and potential returns. As we move forward, we’ll explore how to analyze commodity markets in greater depth to inform your investment decisions.
Analyzing Commodity Markets

A. Supply and demand factors
Supply and demand are the fundamental drivers of commodity prices. Understanding these factors is crucial for successful commodity investing.
Key supply and demand factors include:
- Production levels
- Inventory stocks
- Consumption rates
- Technological advancements
- Weather conditions
| Factor | Impact on Supply | Impact on Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Production | Increased production lowers prices | N/A |
| Inventory | High inventory decreases prices | Low inventory increases demand |
| Consumption | N/A | Higher consumption raises prices |
| Technology | Can increase efficiency and supply | Can create new uses and demand |
| Weather | Extreme conditions can disrupt supply | Can affect seasonal demand |
B. Economic indicators to watch
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into commodity market trends. Investors should monitor:
- GDP growth rates
- Inflation rates
- Interest rates
- Currency exchange rates
- Industrial production indices
These indicators can signal changes in commodity demand and overall economic health, influencing prices across various sectors.
C. Geopolitical influences
Geopolitical events can have significant impacts on commodity markets, often leading to rapid price fluctuations. Key factors include:
- Trade agreements and disputes
- Political instability in resource-rich regions
- Sanctions and embargoes
- Changes in government policies
Investors must stay informed about global political developments to anticipate potential market shifts.
D. Seasonal patterns
Many commodities exhibit predictable seasonal patterns due to natural cycles and consumer behavior. Examples include:
- Agricultural products: Harvest seasons affect supply
- Energy commodities: Heating oil demand increases in winter
- Precious metals: Jewelry demand spikes during holiday seasons
Understanding these patterns can help investors time their trades more effectively.
Now that we’ve explored how to analyze commodity markets, let’s look at practical steps for investing in commodities. Getting started with commodity investing is easier than you might think.
Getting Started with Commodity Investments

Setting investment goals
Before diving into commodity investments, it’s crucial to establish clear and realistic goals. Consider the following aspects when setting your investment objectives:
- Time horizon
- Risk tolerance
- Expected returns
- Portfolio diversification
Here’s a table to help you align your goals with different commodity investment strategies:
| Goal | Time Horizon | Risk Tolerance | Suitable Commodities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital preservation | Short-term | Low | Gold, Silver |
| Income generation | Medium-term | Moderate | Energy, Agriculture |
| Growth | Long-term | High | Industrial Metals, Rare Earths |
Choosing a brokerage platform
Selecting the right brokerage platform is essential for successful commodity investing. Consider these factors when evaluating your options:
- Commission fees
- Available commodity products
- Research and analysis tools
- User interface and mobile app
- Customer support
Creating a balanced portfolio
A well-balanced commodity portfolio can help mitigate risks and maximize potential returns. Here are some tips for diversification:
- Spread investments across different commodity sectors
- Consider both physical commodities and commodity-related stocks
- Include a mix of cyclical and non-cyclical commodities
- Allocate a portion to commodity ETFs or mutual funds
Monitoring and adjusting your investments
Regularly reviewing and rebalancing your commodity portfolio is crucial for long-term success. Key aspects to monitor include:
- Market trends and economic indicators
- Supply and demand dynamics
- Geopolitical events affecting commodity prices
- Performance of individual holdings
As you gain experience, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions about your commodity investments. Remember to stay informed about market developments and be prepared to adjust your strategy as needed.
👉 Stay updated with real-time commodity news at MarketWatch Commodities
Advanced Commodity Trading Techniques
Options trading
Options trading in commodities offers sophisticated strategies for investors. Here are key aspects:
- Call options: Right to buy at a specific price
- Put options: Right to sell at a specific price
- Strike price: Predetermined price for the option
- Expiration date: When the option contract ends
| Option Type | Risk Level | Potential Reward |
|---|---|---|
| Long Call | Limited | Unlimited |
| Long Put | Limited | High |
| Short Call | Unlimited | Limited |
| Short Put | High | Limited |
Spread trading
Spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling related commodity contracts. Benefits include:
- Reduced risk exposure
- Potential for profit in various market conditions
- Lower margin requirements
Common spread strategies:
- Calendar spreads
- Inter-commodity spreads
- Processing spreads
Hedging strategies
Hedging helps protect against adverse price movements:
- Direct hedging: Taking opposite positions in the same commodity
- Cross hedging: Using related commodities or financial instruments
- Rolling hedge: Continuously adjusting hedge positions
Effective hedging requires:
- Thorough market analysis
- Understanding of correlation between assets
- Careful monitoring and adjustment of positions
Now that we’ve explored advanced techniques, let’s examine the tax implications of commodity investing to round out your knowledge.
Tax Implications of Commodity Investing

Capital gains considerations
When investing in commodities, understanding the tax implications is crucial. Capital gains from commodity investments are typically subject to taxation, but the rates can vary depending on several factors:
- Short-term vs. Long-term gains
- Type of commodity investment
- Individual tax bracket
Here’s a breakdown of capital gains considerations:
| Holding Period | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| ≤ 1 year (Short-term) | Ordinary income tax rate |
| > 1 year (Long-term) | 0%, 15%, or 20% (based on income) |
• Physical commodities are often taxed as collectibles (28% maximum rate)
• Futures contracts have special 60/40 tax treatment
• ETFs and mutual funds may have different tax implications based on their structure
Reporting requirements
Accurate reporting of commodity investments is essential to stay compliant with tax laws. Key reporting requirements include:
- Form 1099-B: Received for most commodity trades
- Schedule D: Used to report capital gains and losses
- Form 8949: Detailed reporting of individual transactions
- Form 6781: Specific to futures and options contracts
It’s crucial to keep detailed records of all transactions, including purchase dates, sale dates, and associated costs.
Tax-efficient investment vehicles
To optimize your commodity investments from a tax perspective, consider these tax-efficient vehicles:
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
- Mutual Funds
- Limited Partnerships (LPs)
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Each of these options offers unique tax advantages. For instance, commodity ETFs that hold futures contracts may qualify for lower long-term capital gains rates, even on short-term trades. Always consult with a tax professional to determine the most suitable approach for your specific situation.
Lets Sum It Up

Investing in commodities can be a valuable addition to your portfolio, offering diversification and a potential hedge against inflation.
From understanding the basics of commodities to exploring different investment options and strategies, this guide has provided a full beginner-friendly overview.
By analyzing commodity markets, starting with low-risk options, and gradually moving into more advanced commodity trading techniques, you can build a strong foundation in investing in commodities.
As you embark on your commodity investing journey, remember to stay informed about market trends, global events, and tax implications. Always conduct thorough research, consider your risk tolerance, and consult with financial professionals when needed.
With patience, knowledge, and a well-thought-out strategy, commodity investing can become a rewarding part of your overall financial plan. The Investillect blog has even more strategies to level up your financial game.